Table of Contents
Over the past decades, the keto diet (often simply called “keto”) has attracted the attention of both the scientific community and the public as one of the most discussed strategies for improving health and weight management. Although it has a long history, especially in the treatment of epilepsy in children, the application of keto nutrition as a means of improving overall health is a relatively new phenomenon.
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and low-carbohydrate eating plan. Its main idea is to encourage the body to enter a state of ketosis, a process in which, due to the lack of carbohydrates, the body begins to use fats as the main source of energy, producing ketones in the liver. This state is key to understanding the numerous potential health benefits associated with the keto diet.
General Principles of Ketogenic Nutrition
The keto diet focuses on high fat intake – typically about 70-80% of the total daily caloric intake, an average of about 20% protein, and a very limited amount of carbohydrates, usually under 50 grams per day. The body enters a state of ketosis, where fats are broken down in the liver into ketone bodies, which serve as an alternative energy source.
The Effects of Ketosis
The metabolism is reconfigured to burn fats, leading to weight loss and a reduction in body fat. Blood insulin levels typically decrease as the need for it to process glucose is reduced. Many people experience more stable energy levels and a reduced feeling of hunger.
Maintaining this state requires strict adherence to a diet that includes foods such as meat, fatty fish, eggs, butter, cheeses, nuts, seeds, some fatty dairy products, and selected low-carbohydrate vegetables.
Mechanism of the Metabolic Process in Ketosis
- Reduction of Glycogen Reserves. When carbohydrate intake is restricted, the body begins to deplete its reserves of glycogen, stored in the liver and muscles. Glycogen is a form of glucose storage.
- Mobilization of Fats. With the reduction of glycogen reserves, the body switches to using fats for energy. Triglycerides stored in fat cells (adipocytes) are broken down in a process called lipolysis, releasing fatty acids into the blood.
- Production of Ketones. The liver transforms the free fatty acids into ketones through a process called “ketogenesis.” These ketone bodies include acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone.
- Utilization of Ketones for Energy. Ketones are transported to various tissues, including the brain, where they serve as an alternative energy source in the absence of glucose.
- Metabolic Changes. Ketosis leads to a number of metabolic changes, including reduced insulin production by the pancreas and increased gluconeogenesis (glucose production) in the liver from non-carbohydrate sources.
In this article, we will examine the basic principles of ketogenic nutrition, its potential benefits and challenges. We will understand how it affects various aspects of health, including weight management, brain function, and long-term health. We will also discuss the psychological aspects of maintaining this nutritional regimen.

Maintaining Motivation
The transition to and maintenance of a ketogenic diet represents not only a physical, but also a significant psychological challenge. The mental aspects of strictly adhering to the regime require careful consideration.
Psychological Aspects of a Strict Diet
For many, implementing a keto diet requires significant changes in eating habits, which can be psychologically difficult. Such changes often involve giving up convenient and familiar foods, leading to a sense of deprivation and difficulties in family and social gatherings. Effects of the “keto flu”, such as fatigue and irritability, in the initial period can further complicate the adaptation to the regime.
Strategies for Maintaining Motivation
To maintain motivation while on a diet, it is important to develop clear and achievable goals. It is appropriate to start with short-term intentions, such as following the diet for a week, or long-term ones – improving overall health. Self-monitoring, through keeping a diary of food intake and achievements, is useful for consistency, accountability, and visibility of results.
Anyone who has ever been on a diet knows how important support from family and friends is. Teasing and misunderstanding from others can completely derail the plan. Building a supportive social network, which includes relatives, friends, or online communities, is essential. This support can provide the necessary motivation and help in sharing recipes and strategies for coping with challenges.
Starting a strict diet requires flexibility and realistic expectations. It’s normal to face temptations and occasionally deviate from the strict adherence to the regimen. In such cases, simply return to it as quickly as possible, without feeling guilt or failure.
For maintaining mental well-being and managing stress, engage in positive activities like meditation, yoga, or light physical exercises. If you encounter serious resistance in yourself or from others, it’s a good idea to seek professional help from a psychologist or nutritionist, who can advise you on your healthy and balanced approach to the keto diet.
Benefits of the Keto Regime
While the ketogenic diet is often associated with weight loss, substantial scientific evidence supports the claim that it offers important benefits for brain health. These manifest through improvement in cognitive functions and potentially positive impact on various neurological conditions.
Impact of the Keto Diet on Cognitive Functions
The ketogenic diet alters the way the brain and body process energy, using ketone bodies instead of glucose. This energy switch can have a positive effect on cognitive functions, including improved concentration and better memory. Studies show that ketones may be a more efficient and stable energy source for the brain, leading to improvements in cognitive abilities, especially in older individuals.

Benefits for Brain Health
The keto diet has been studied in the context of various neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. The regimen has shown potential to slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, reduce the frequency and severity of epileptic seizures, and even improve cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s patients. Numerous preliminary studies indicate that the ketogenic diet can positively affect nerve inflammation associated with various neurological diseases.
A recent review highlighted the diverse benefits of low-carbohydrate, high-fat diets like the ketogenic diet. These benefits include assistance in weight reduction, reversing signs of metabolic syndrome, minimizing or eliminating the need for insulin in type II diabetics, reducing inflammation, improving epigenetic profiles, altering the microbiome, and improving lipid profiles.
These studies demonstrate a wide range of potential health benefits, exceeding the commonly accepted role of keto in weight management. Ongoing research continues to reveal new possibilities for using the diet as a therapeutic tool in neurology and psychiatry.
Keto and Longevity – Impact on Aging
Studies on the impact of the ketogenic diet on aging processes are another important aspect. According to research by UC Davis Health, the ketogenic diet improves muscle function in older animals, preventing age-related muscle mass loss (sarcopenia)[“”].
The same study shows that both exercise and the keto diet can increase the number of mitochondria in muscles, leading to better ability of muscles to produce energy from fats, improving the breakdown of potential neurotoxins. This prevents their penetration into the brain and protects it from cellular loss.
Overcoming the Keto Flu
“Keto flu” is a term summarizing the symptoms some people experience when transitioning to a ketogenic diet. They often include headache, fatigue, nausea, and dizziness. They are usually due to the body’s transition from burning carbohydrates to using fats for energy, as well as dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
To reduce the side effects of the keto flu and ease the transition to ketogenic eating, follow these recommendations:
- Drink more water. Increase fluid intake to overcome dehydration and related symptoms like headache and dizziness.
- Ensure quality sleep. Improving the quality and quantity of sleep can help combat fatigue and reduce food cravings.
- Salt your food. Adding a little more salt to your food can help restore lost electrolytes and improve water retention in the body.
- Drink electrolytes: Maintaining balance through foods and drinks enriched with electrolytes is essential. You may include magnesium supplements and sugar-free sports drinks.
Connection between Nutrition and Mental Health
Keto is used not only for weight management but also as a therapy for various psychiatric and neurological disorders. The diet has shown promising results in treating such conditions, leading to significant interest in its potential benefits for mental clarity and mental health.
The regimen affects several biological processes, such as mitochondrial energy metabolism, inflammatory processes, oxidative stress, monoaminergic activity, and progression of neurodegeneration, therefore it is considered a metabolic therapy.
Research by Kraeuter et al. (2015, 2019c) found that the ketogenic diet prevents schizophrenia-like abnormal behaviors induced by acute administration of MK-801, including hyperactivity, stereotypical behaviors, reduced sociability, working memory deficit, and impaired pre-pulse inhibition of the startle reflex in male mice.
It is also indicated that the ketogenic diet may serve as a therapeutic option for people with psychiatric disorders, thus contributing to the understanding of its impact on mental health. Neurophysiological changes in the cognitive brain, in response to ketosis, are described in various neuroimaging studies to visually represent the effect on the brain beyond purely molecular explanations.
Myths and Facts About the Keto Regime
The ketogenic diet is subject to many myths and misunderstandings, based on decades of misinformation and controversies in the field of nutrition. Let’s examine some of these myths and present the facts and scientific data to correct the misconceptions.
- Myth: The Keto Diet Leads to Much Higher Fat Consumption. Findings from clinical trials show that this is not always the case, as in many instances the total amount of fats does not increase significantly.
- Myth: You Must Eat Fats to Burn Body Fat. The idea that consuming fats leads to burning body fat is incorrect. In fact, an important aspect of weight loss and improving insulin resistance is reducing insulin levels, allowing the body to use stored fats for energy. Dietary fats have a small effect on insulin levels in the short term.
- Myth: Fats are the Most Satiating. While fats help regulate appetite, there is a significant amount of evidence that proteins and fibers have a stronger effect on the feeling of fullness.
- Myth: Fats Cannot Lead to Weight Gain on a Keto Diet. The claim that fats do not lead to weight gain, even on a low-carbohydrate diet, is incorrect. The long-term effects of dietary fats on insulin resistance and weight are still not fully clarified.
Keto for Athletes – Enhancing Performance
Research on the impact of the ketogenic diet on athletic performance leads to diverse conclusions.

Impact of Keto on Athletic Performance
- Studies show that after 3-4 weeks of adaptation to a keto regime, endurance-trained athletes maintain their capabilities during moderate (46-63% VO2max) and intense (64-90% VO2max) training. However, at intensities >70% VO2max, the increase in fat oxidation is associated with reduced efficiency (increased oxygen consumption), in some cases also with an increased perception of effort and heart rate [“”].
Tips for Athletes and Active People
- It’s important for athletes who decide to undergo a keto regime to adapt gradually and closely monitor their physical condition, especially during the first few weeks.
- It is essential to ensure adequate intake of proteins and electrolytes to avoid muscle mass reduction and to maintain optimal hydration levels.
Examples and Recommendations
- Research indicates that the keto diet can be effective in sports requiring short-term intense activity, such as sprinting. On the other hand, for sports requiring high oxygen efficiency, the keto diet may not be the best choice.
- The intake of keto foods should be individually adapted, considering the specific needs and goals of each athlete, as well as the characteristics of the performed sports disciplines.
The ketogenic diet may offer certain advantages for athletic performance, but it is important to approach it with understanding and attention to individual needs and body reactions.
Keto Recipes – Appetizer, Main Course, and Dessert
Some of the most popular low-carbohydrate recipes include avocado, asparagus, salmon, and chicken. The suggested recipes combine these “bestsellers,” and the dessert is an irresistible chocolate treat with only 5g of carbohydrates.
Keto Chicken and Avocado Salad
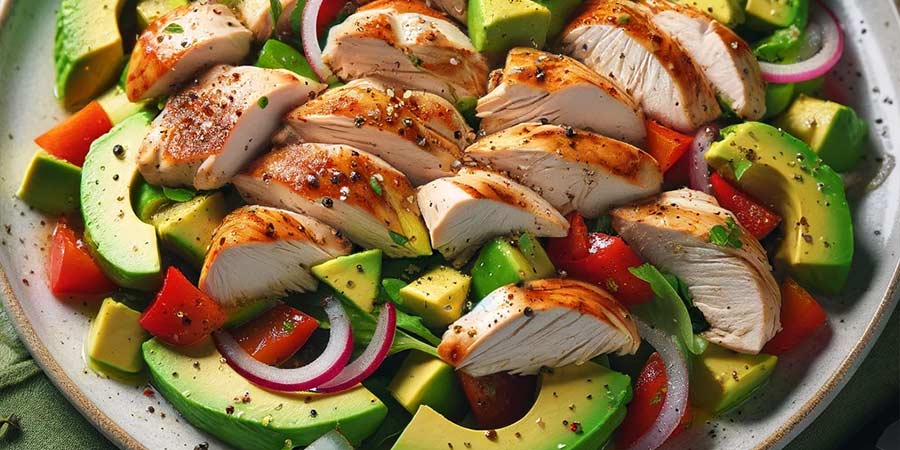

- Ingredients: 2 medium-sized avocados, 200g roasted chicken meat, 1 red pepper, 1/2 onion, 2 tbsp olive oil, 1 tbsp lemon juice, salt and black pepper to taste.
- Preparation: Finely chop the avocado, chicken, pepper, and onion. Mix in a bowl. Add olive oil, lemon juice, salt, and pepper. Stir well.
- Nutritional Values (per serving): calories: about 350, fats: 25g, carbohydrates: 10g (net), proteins: 20g.
Keto Salmon with Asparagus and Lemon Sauce
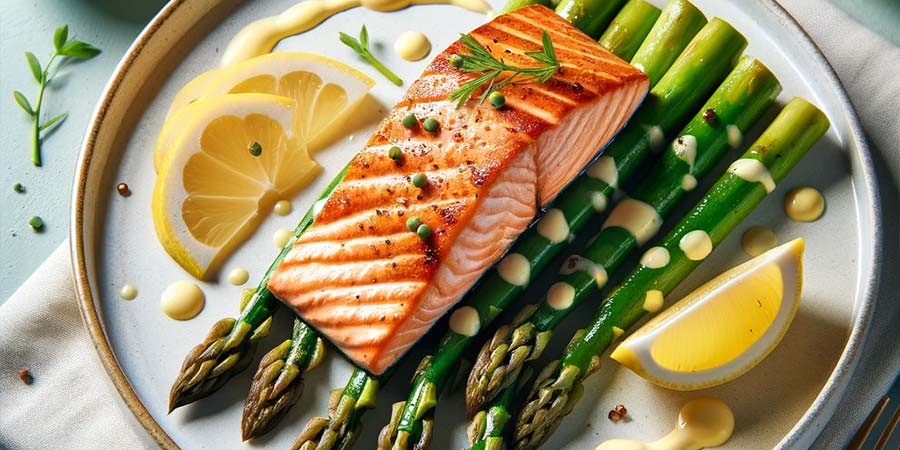

- Ingredients: 4 salmon fillets (about 150-200g each), 1 bunch of asparagus, 2 tbsp butter, 1 lemon, salt, black pepper, garlic powder.
- Preparation: Coat the fish with butter, sprinkle with salt, black pepper, and garlic powder. Place in a baking dish. Add the chopped asparagus on the side. Sprinkle everything with lemon juice. Bake in a preheated oven at 200°C for about 15-20 minutes.
- Nutritional Values (per serving): calories: about 400, fats: 25g, carbohydrates: 5g (net), proteins: 35g.
Keto Chocolate Brownie
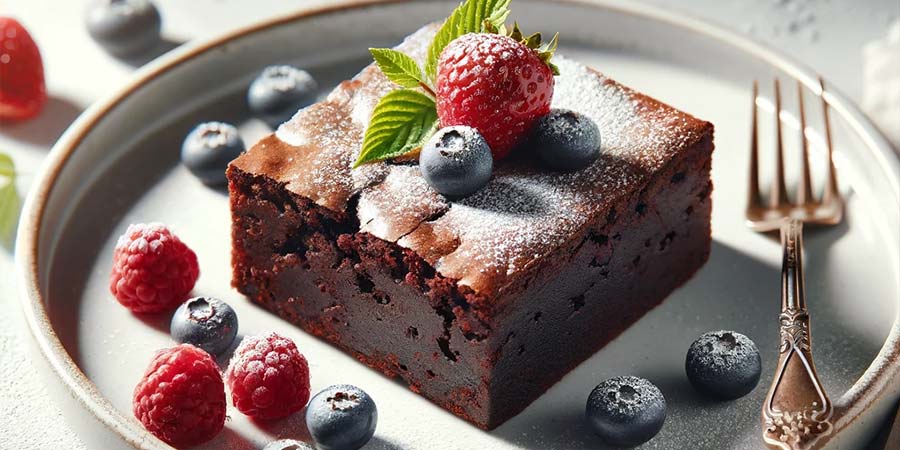

- Ingredients: 200g dark chocolate (at least 70% cocoa), 100g coconut oil, 3 eggs, 100g xylitol, 50g coconut flour, 1 tsp baking powder, a pinch of salt.
- Preparation: Melt the chocolate and coconut oil in a double boiler. Beat the eggs with xylitol until fluffy. Add the melted butter and chocolate to the eggs. Add the coconut flour, baking powder, and salt. Mix well. Pour into a greased pan and bake in a preheated oven at 180°C for about 20 minutes.
- Nutritional Values (per serving): Calories: about 250, Fats: 20g, Carbohydrates: 5g (net), Proteins: 4g.
These recipes are in line with the keto regime, providing a richness of fats and minimal carbohydrates to maintain a state of ketosis.
10 Keto Foods – Carbohydrate, Fat, and Protein Content*
| Food Type | Carbohydrates (g) | Fats (g) | Proteins (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avocado | 9 | 15 | 2 |
| Salmon | 0 | 13 | 20 |
| Coconut Oil | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Almonds | 22 | 49 | 21 |
| Spinach | 3.6 | 0.4 | 2.9 |
| Chicken Breast | 0 | 3.6 | 31 |
| Ground Beef (80% fat) | 0 | 20 | 17 |
| Eggs | 1.1 | 9.5 | 13 |
| Olives | 6 | 11 | 1 |
| Cheddar Cheese | 1.3 | 33 | 25 |
Vegetables to Avoid
In the ketogenic diet, the goal is to limit carbohydrate intake, which means avoiding vegetables high in carbohydrates. Typically, we consider all vegetables suitable for a diet. However, with the keto regime, this is not the case. Here is a list of some vegetables to avoid on a keto regime:
- Potatoes
- Sweet Potatoes
- Corn
- Peas
- Red Bell Pepper
- Carrots
- Onions
- Beets
- Parsnips
- Zucchini
These foods are higher in carbohydrates and can disrupt the state of ketosis. Instead, consumption of vegetables with lower carbohydrate content is recommended, such as spinach, broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, and lettuce.
The ketogenic diet has significant potential for improving health and managing weight, offering an alternative approach to nutrition. From a psychological perspective, adhering to it requires significant adaptation and motivation. Its impacts on brain health and slowing the aging process represent important areas for future research.
Further observations are needed on the long-term effects of the regime for different aspects of health and athletic performance. Many myths and prejudices still exist that need further debunking with scientific evidence.
*Before starting any diet or nutritional regimen, consult a healthcare professional, especially during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or if you have any illnesses.